Why in the News?
A powerful magnitude 8.8 earthquake struck near Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula which is part of the seismically active Pacific Ring of Fire triggering tsunami waves that hit coastal towns in Russia and Japan.
More on the news
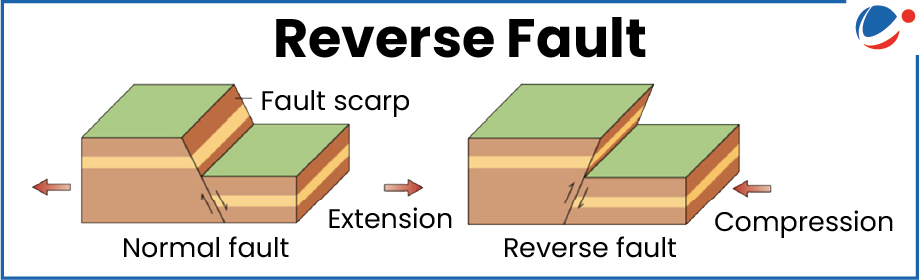
- Scientists believe the quake was caused by shallow reverse faulting.
- Reverse faulting (or thrust faulting) occurs when one block of Earth's crust is pushed up over another due to compressional forces.
- "Shallow" Reverse faulting means rupture occurred near the Earth's surface.
- It can cause strong ground shaking, powerful aftershocks, tsunamis, and serious damage to infrastructure.
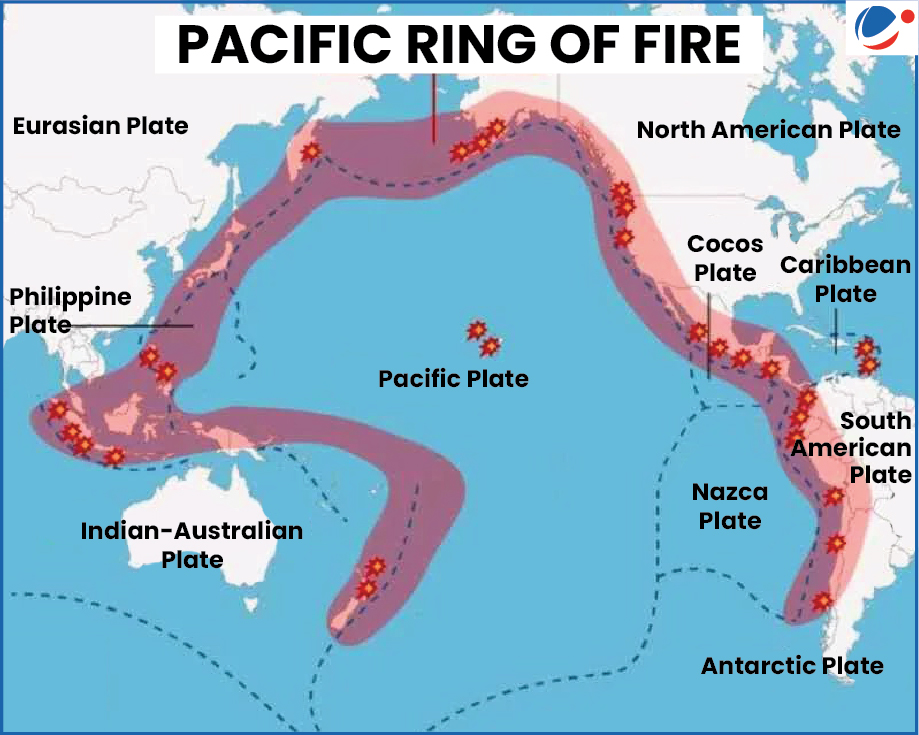
About Pacific Ring of Fire
- Also referred as Circum-Pacific Belt, It is a horseshoe-shaped belt of intense seismic and volcanic activity encircling the Pacific Ocean basin.
- It accounts for:
- ~75% of the world's active volcanoes
- ~90% of the world's earthquakes
- Location & Extent
- Extends for ~40,000 km around the Pacific Ocean.
- It traces boundaries between several tectonic plates including the Pacific, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, Indian-Australian, Nazca, North American and Philippine Plates.
Features of Circum-Pacific Belt
- Geography: It has led to the formation of mountains, island arcs, deep underwater trenches, like the Mariana Trench (world's deepest spot).
- Source of geothermal energy: More than 40% of global geothermal energy resources are stored in that region.
- Minerals: Home to many rich mineral deposits, such as gold, copper, molybdenum, and other metals.
- Agricultural Significance: Volcanic soils are fertile (good for crops like rice, coffee)
Cause of Frequent Earthquakes and Volcanism along pacific ring of fire
- Subduction zones: Along Ring of Fire, tectonic plates overlap at convergent boundaries called subduction zones where the lower plate is pushed down by the upper plate.
- Subducted rock melts into magma near earth surface, an ideal condition for volcanic activity. E.g. Taupo Volcanic Arc, near New Zealand where dense Pacific Plate is subducting beneath Australian Plate.
- Zone of transform boundary/fault: In places like the San Andreas Fault (California), plates slide past each other laterally. This shearing motion causes powerful earthquakes but little volcanism.
- Mid-oceanic Ridges/Divergent Boundaries: Tectonic plates pulling apart create seafloor spreading and rift valleys.
- E.g. East Pacific Rise exemplifies major seafloor spreading in Ring of Fire, located where Pacific Plate diverges from Cocos, Nazca, and Antarctic Plates, featuring both volcanism and hydrothermal vents.
- Hot Spots: Areas deep in Earth's mantle where rising heat melts rock in the upper mantle. This magma pushes through crustal cracks to form volcanoes.
Conclusion
The Ring of Fire exemplifies Earth's dynamic geology, where converging tectonic processes create the vast majority of global volcanic eruptions and seismic activity, profoundly shaping Pacific civilizations and ecosystems.






