Front Running
SEBI notifies norms for mutual funds for preventing fraudulent transactions and front running.
Front Running
- Refers to usage of non-public information to directly or indirectly buy or sell securities, or enters into options or futures contracts, in advance of a substantial order. (Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI))
- It undermines confidence in the financial markets and creates an uneven playing field for other investors.
- It is illegal in India.
- Tags :
- SEBI
- Front Running
- Mutual Funds
White Category Sectors
White category sectors will now not require prior permission of the state pollution control boards to establish and operate under the Air Act, 1981 and Water Act, 1974.
- The permissions officially known as ‘consent to establish’ (CTE) and ‘consent to operate’ (CTO) are granted to regulate industries that discharge effluents or emit pollutants into the environment.
- White category industries will have to inform SPCBs through self-declarations.
White Category Sectors
- Those industries which are practically non-polluting are categorised under the ‘white category’ by the Central Pollution Control Board.
- It includes Wind and solar power projects, assembly of air coolers, bicycle assembly etc.
- Tags :
- Consent to Establish
- Consent to Operate
- White Category Sectors
- Non-Polluting Industries
Climate Resilient and Biofortified Varieties of Crops Released
Prime Minister released 109 high yielding, climate resilient and biofortified varieties of crops.
- These crops have been developed by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and release of new varieties of crops is the example of a "lab to land" programme.
- ICAR has been running crop-improvement programme to develop new crop varieties and hybrids with wider adaptability and higher yield.
- Crop-improvement process uses different strategies such as
- Genomics-assisted selection
- Phenomics (systematic measurement and analysis of qualitative and quantitative traits)
- Conventional breeding or Biotechnology-based approaches like genetic engineering and genome editing.
Need of Crop Improvement
- Managing Impact of Climate Change: Climate resilient seeds can yield good crop even in adverse weather (heat waves, droughts, etc.). E.g. Bt cotton
- Climate resilient crops will reduce crop losses due to diseases and pests attacks.
- Food Security: Agricultural yields are projected to drop by 16% by 2030 (World Economic Forum).
- Nutritional Security: Government seeks to promote biofortified crops by linking them with the programmes like Mid-Day Meal (PM Poshan Scheme), etc., to make India free from malnutrition.
- Also, these are affordable as biofortified varieties crop does not involve any additional cost on preparing the enriched food grains. E.g. vitamin-A rich maize grains.
- Rising Farmers Income: High-yielding and adaptable crop varieties contribute to higher incomes.
About Biofortification
About Lab to Land programme
|
- Tags :
- Food Security
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
- Biofortified Crops
- Lab to Land Programme
- Nutritional Security
- Climate Resilient Crops
Articles Sources
Open Market Sale Scheme (OMSS) (Domestic)
States can purchase rice from Food Corporation of India (FCI) under the OMSS Domestic without participating in the e-auction from August 1, 2024.
- It aims to reduce the huge surplus of stocks prior to the commencement of the new procurement season.
OMSS – Domestic
- It refers to offering of food grains (wheat & rice) in the open market at prices, fixed by the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution through e-auction.
- It aims to control the price in the market with the aim to curb inflation.
- Tags :
- Open Market Sale Scheme
- Food Corporation of India (FCI)
Articles Sources
NITI Aayog's Report on Seaweed Value Chain
NITI Aayog publishes a report titled “Strategy for the development of Seaweed Value Chain”.
- Seaweeds are numerous types of marine plants and macro algae that thrive in rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water.
- Cultivation of seaweeds are part of aquacultures. Fishing and aquaculture sector contributes 1.5% of India’s GDP.
Significance of Seaweed Farming
- Economic: Valuable for bioactive compounds and applications in food, pharmaceuticals etc.
- Environmental: Important role in Carbon Sequestration & climate resilience.
- Nutrition imperative: Provide vital minerals and Vitamins like A, B1, B12, etc.
Challenges faced by Seaweed Farming

- Lack of a comprehensive policy framework.
- Lack of availability of quality Seeds.
- Ecological concerns (Exotic species impact on biodiversity and coral reefs).
Recommendations For Promoting Seaweed Farming
- Regulatory and governance reforms: Forming National Steering Committee; Priority Sector Lending (PSL) for seaweed, etc.
- Social Security and Financial Support: Providing crop insurances; mobilization of farmers through SHGs etc.
- Infrastructure and institutions: Establishment of seed banks, processing centers, marketing centers etc.
- Tags :
- Aquaculture
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojna (PMMSY)
- Seaweed Value Chain
Global Employment Trends (GET) For Youth 2024 Report
The report by ILO represents the 20th anniversary publication of GET for Youth and focuses on achievements, challenges and outlook for youth employment.
Key Highlights of Report
- Post Covid recovery: Global youth unemployment rate in 2023 is 13%, the lowest in 15 years, and 64.9 million unemployed youth, the lowest since 2000.
- NEET (Not in Employment, Education or Training) Status: 20.4% of youth were in NEET in 2023, indicating broader labour market exclusion.
- 2 in 3 young NEETs are women.
- Global Challenges:
- Inequalities of Opportunity: 4 in 5 young adult workers are in regular paid job in high-income countries, compared to 1 in 5 in low-income countries.
- Regional disparities: Growth in youth labour force in Africa by 2050 while all other regions face contraction.
- Also, 1 in 3 youth in Arab states and North Africa are unemployed.
- Youth well-being concern: Many young people are stressed about job loss, state of economy, and lack of social mobility across generations.
- Educational Mismatch: 2 in 3 young adult workers in developing economies hold qualifications that do not match well to their job.
Recommendations from the report
|
- Tags :
- Global Employment Trends
- NEET (Not in Employment, Education or Training)
Banking Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2024 introduced in Lok Sabha
Amendment has been brought as banking sector has evolved over years, and seeks to improve bank governance.
- Bill proposes to amend RBI Act, 1934, Banking Regulation Act, 1949, SBI Act, 1955, Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Act, 1970 and Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Act, 1980.
Key Provisions of Bill
- Increased Nominees: Allows depositors to nominate up to four nominees simultaneously (With proportion of their shares specified) and successively.
- Successive nomination: Several nominees listed in specific order, nominees would be contacted for claiming funds according to order.
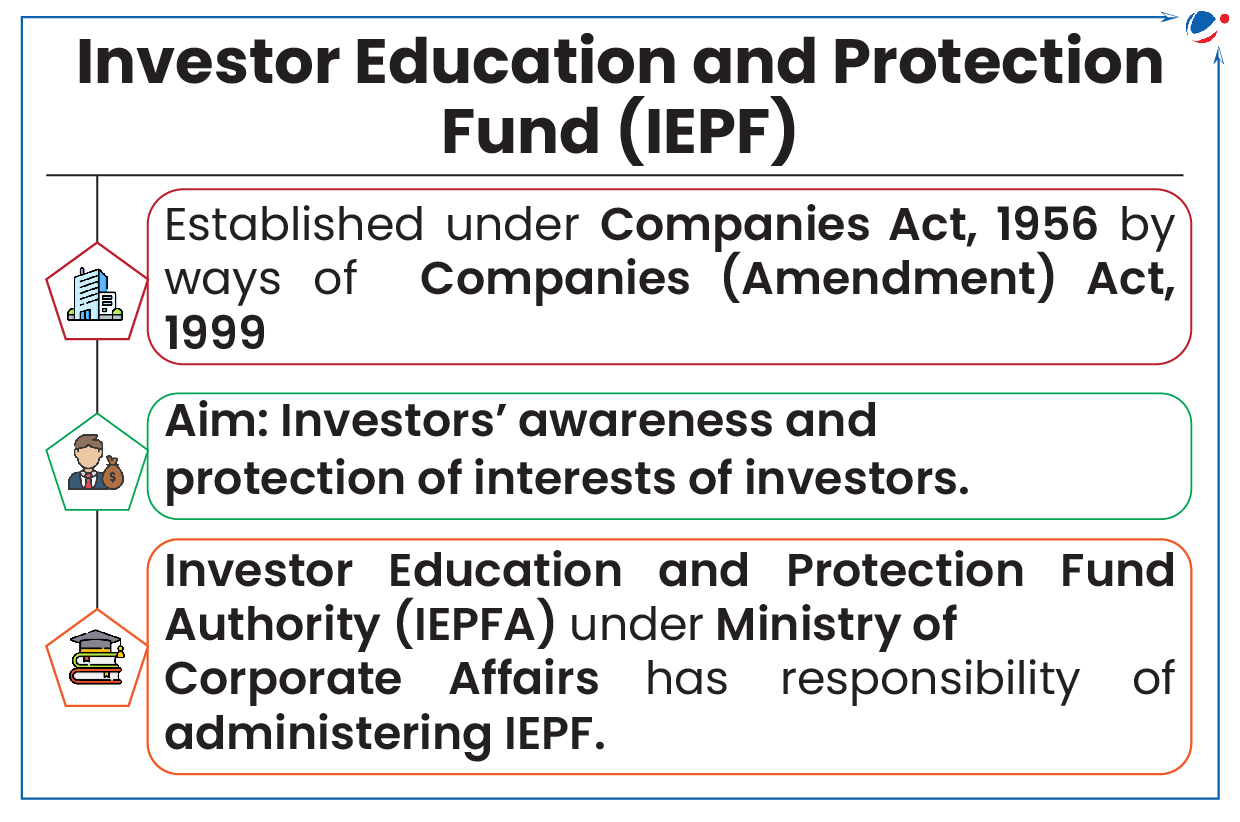
- Investor education and protection fund (IEPF): Enables transfer of unclaimed dividends, shares, and interest or redemption of bonds to IEPF when they remain unclaimed for seven consecutive years.
- Bill allows individuals to claim transfers/refunds from IEPF.
- Substantial interest in shareholding: Threshold in shareholding has been increased from Rs 5 lakh to Rs 2 crore for directorships.
- Provision for Cooperative Banks:
- Extends tenure of directors in cooperative banks from 8 years to 10 years.
Significance
- Provide consistency in reporting to RBI
- Reduce unclaimed deposits (over ₹42,000 crore in march 2023) by increasing nominee number.
- Unclaimed deposits are balances in savings/current accounts that are not operated for 10 years, or term deposits not claimed within 10 years from date of maturity.
- Tags :
- Banking Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2024
- Investor Education and Protection Fund (IEPF)
Grain ATM
WFP and Government of Odisha Jointly launched 24/7 'Grain ATM' in Bhubaneswar.
- India's first 24/7 'Grain ATM,' called 'Annapurti,' will be set up across Odish to provide food grains to beneficiaries with 24/7 access under the National Food Security Act (NFSA).
- NFSA entitles up to 75% of the rural population and 50% of the urban population to receive subsidized food grains.

About Annapurti
- It is a Made-in-India product (designed and developed by WFP India)
- It dispenses the type and quantity of the selected grain (wheat, rice or millet) to each beneficiary, after biometric authentication.
- It can provide universal access to food grains and reduce the waiting time by 70%.
- It is energy efficient and can be connected to solar panels for automatic refilling.
- At the 2022 WFP Innovation Awards, it was recognized as one of the WFP’s top 5 innovative solutions for disrupting hunger.
- Tags :
- National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013
- Grain ATM
- Annapurti
- UNWFP
Jan Poshan Kendras
Union Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution launched pilot project for transformation of 60 Fair Price Shops (FPS) into Jan Poshan Kendras.
- FPSs are shops licensed to distribute essential commodities issued under the Essential Commodities Act (1955) to the ration card holders under Targeted Public Distribution System.
About Jan Poshan Kendras
- Kendras will offer a diverse range of nutrition-rich food items to consumer as well as provide an additional source of income to the FPS dealers.
- They have to store 50% products under the category of nutrition while the rest for keeping other household items.
- The pilot will cover states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Telangana, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Tags :
- Jan Poshan Kendras
- Targeted Public Distribution System
- Fair Price Shops (FPS)
- Essential Commodities Act (1955)
Bharatiya Vayuyan Vidheyak 2024 Introduced in the Lok Sabha
It will replace the 90-year-old Aircraft Act, 1934 (for the control of the manufacture, possession, use, operation, sale, import and export of aircraft).
Key Highlights of the Bill
- Aim: To address the ambiguities in the existing law and for ease of doing business & manufacturing in aviation sector.
- Important Provisions:
- To empower the Central Government to make rules to implement the Convention relating to international civil aviation.
- E.g., Chicago Convention (1944) and the International Telecommunication Convention (1932).
- To give the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS), and the Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB) increased powers.
- To empower the Central Government to issue orders (like detaining aircraft) in emergency in the interest of public safety.
- To empower the Central Government to make rules to implement the Convention relating to international civil aviation.
- Tags :
- Aircraft Act, 1934
- Bharatiya Vayuyan Vidheyak 2024
- Aviation sector
QCI Surajya Recognition & Ranking Framework
Quality Council of India (QCI) introduced QCI Surajya Recognition & Ranking Framework.
About Framework
- It aims at recognising and rewarding states and organizations that excel in quality and innovation to achieve the aim of a Developed (Viksit) India.
- It is categorized under four pillars:
- Shiksha (Education),
- Swasthya (Health),
- Samriddhi (Prosperity), and
- Sushasan (Governance).
About QCI
- It was established as the national body of accreditation in 1996 and is an autonomous non-profit organization under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Based on the recommendation of the Expert Mission of European Union.
- It was jointly set up by the Government of India and the Indian Industry (ASSOCHAM, FICCI, CII).
- Nodal Department: Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Governing Council:
- 39 members including the Chairperson and Secretary General with equal representation of Government, Industry and other Stakeholders.
- Chairperson is nominated by the Prime Minister.
- Role of QCI
- National Accreditation Body (NAB): To promote quality through the National Quality Campaign in line with global standards.
- Create a mechanism for third-party assessment of products, services and processes.
- Improve the quality of life and wellbeing of the citizens of India.
- Tags :
- Quality Council of India
- QCI Surajya Recognition & Ranking Framework
- eQuest
- Accreditation
Articles Sources
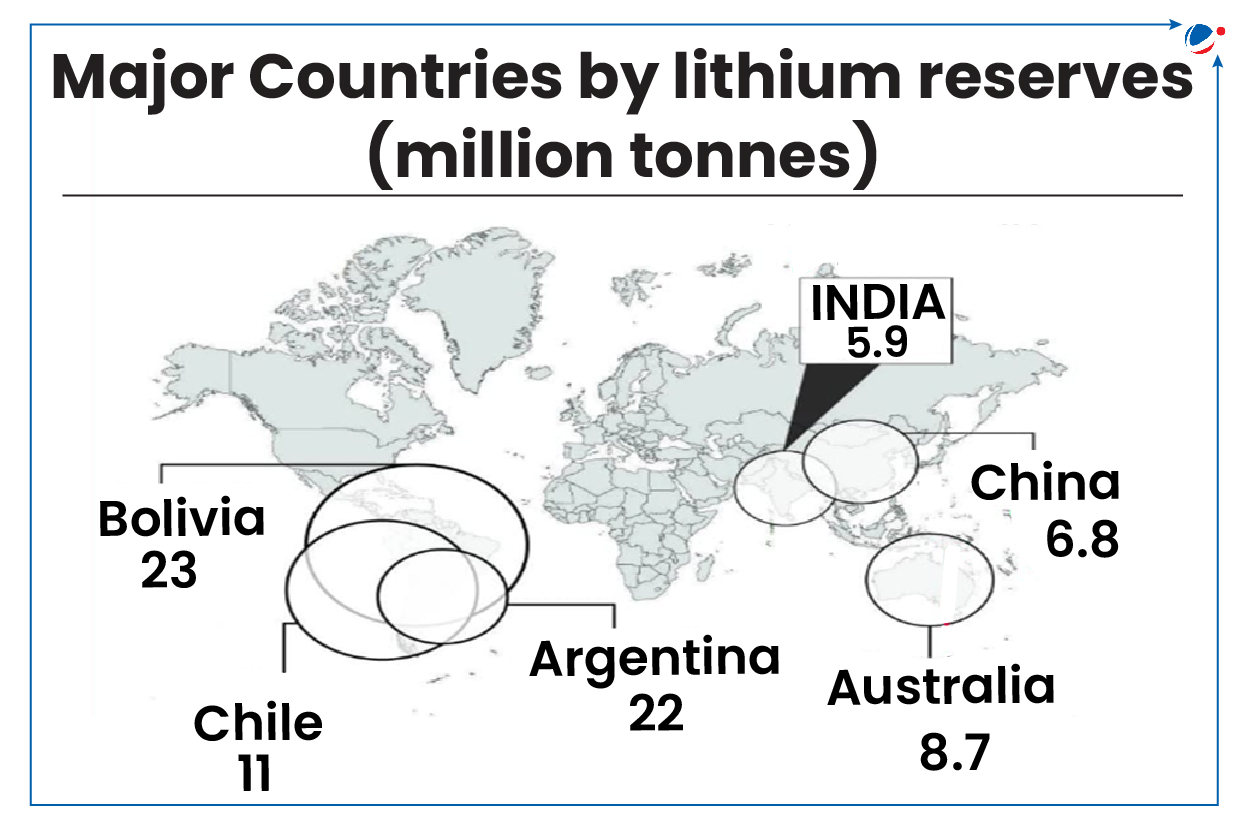
Lithium reserves in India
Atomic Minerals Directorate for Exploration and Research has established 1,600 tonnes of Lithium resources in Mandya district.
- Lithium reserve discovery will lead to
- Reduced Import Dependence (Currently India majorly depends on China and Hong Kong)
- self-sufficiency in energy storage needs & Green transition
- Industrial development E.g. Vehicle and automobile industry development
About Lithium (white gold)
- Lithium is a soft, silvery-white alkali toxic metal and has the lowest density of all metals.
- It has been identified as critical and strategic minerals under Mines and Mineral (Development and Regulation) (Amendment) Act 2023.
Applications of Lithium
- Batteries: Rechargeable Li-Ion batteries for mobile phones, EVs etc. and non-rechargeable batteries for heart pacemakers, clocks etc.
- Alloys: Alloyed with aluminum and magnesium to improve strength and reduce weight e.g. armor plating, aircraft, bicycle frames, and high-speed trains etc.
- Industrial Use: Used in air conditioning, industrial drying systems and glass ceramics.
Steps Taken
- KABIL explores strategic minerals in overseas territories.
- Australia India Critical Minerals Investment Partnership
- Geological Survey of India (GSI) is exploring Lithium reserves in India.
- Ministry of Mines joined Mineral Security Partnership (MSP) led by USA.
- Tags :
- Lithium
- Lithium-Ion Battery
- Critical and Strategic Minerals
- Lithium reserves
Articles Sources
Tantalum
Central Government notified Tantalum as a Critical and Strategic Mineral under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
About Tantalum
- Tantalum is a rare metal with the atomic number 73
- It’s grey, heavy, very hard, and corrosion-resistant.
- Characteristics:
- When pure, tantalum is ductile (can be stretched, pulled, or drawn into a thin wire).
- Extremely high melting point.
- Uses: Making capacitors in electronic devices, surgical equipment & implants, components for chemical plants, nuclear power plants, aeroplanes and missiles etc.
- Tags :
- critical and strategic minerals
- MMDRA, 1957
- Tantalum



