Why in the News?
In 2025 India's renewable energy sector achieved two historic milestone- renewable energy met 51.5 % of total electricity demand (July 2025) and share of installed electricity capacity of non-fossil fuel sources reached 51 % (September 2025).
About Renewable energy (RE)
- It is energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed, e.g., Solar Energy, Wind Energy, Geothermal Energy, Hydro Power, Ocean Energy, Bio Energy.
- India's key targets for renewable energy sector:
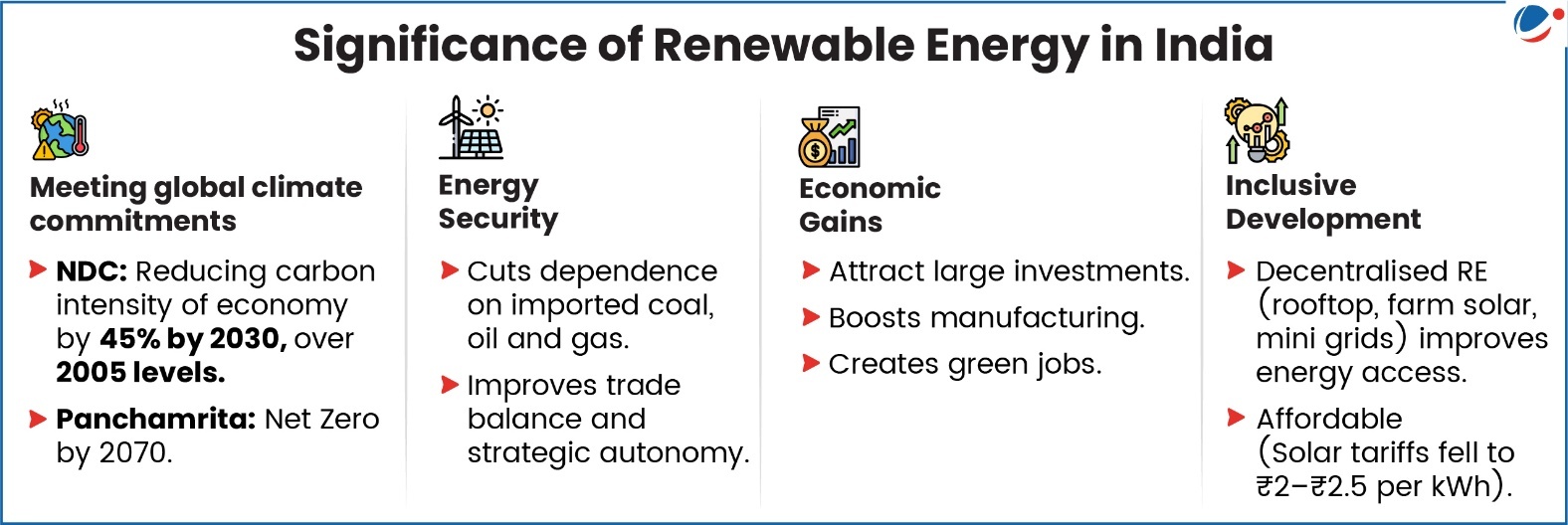
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) target (Updated in 2022)
- Achieving 50% of cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources by 2030 (achieved five years ahead).
- Panchamrita targets (for 2030)
- Meet 50% of energy requirements from renewable energy
- Reach non-fossil energy capacity of 500 GW
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) target (Updated in 2022)
Status of India's Renewable Energy (RE) sector

- Installed electricity capacity of non-fossil fuel sources (renewable energy, hydro, and nuclear): 256.09 GW (September 2025) (see infographic for energy-wise breakdown)
- Global Ranking (IRENA RE Statistics 2025): 4th in Renewable Energy Installed Capacity; 4th in Wind Power; 3rd largest ethanol producer and 3rd in Solar Power capacity.
- Progress:
- ~3 times increase in Installed RE capacity (2014 to 2025).
- ~40-fold increase in Solar energy (2014 to 2025).
- 30% increase in Wind energy capacity (2020-2024).
- 13-fold increase in Ethanol blending in petrol (1.5% in 2014 to 20% in 2025).
- Top 5 RE states: Rajasthan, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Maharashtra.
Reason behind growth in Renewable Sector
- High potential: E.g., Tropic of Cancer passes through many states, giving 300+ sunny days annually; High wind energy potential due to long coastline and elevated terrains etc.
- Supportive Government Policies and Initiatives:
- National policies for long term planning: E.g., Offshore Wind Energy Policy, 2015; National Wind–Solar Hybrid Policy, 2018; National Policy on Biofuels, 2018 etc.
- Development of Infrastructure: Green Energy Corridor (GEC) scheme for transmission infrastructure; PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana providing subsidized rooftop solar panels installation (10 Lakh Installations as of March 2025) etc.
- Regulatory & Market Reforms:
- Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO): Mandates that states and utilities must procure a minimum percentage of their electricity from renewable sources.
- Indian Carbon Market (2024): A carbon trading platform with Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS), notified under Energy Conservation Act, 2001 to incentivize low-carbon power generation.
- Green Open Access Rules (2022): Allow large consumers to buy renewable energy from any source nationwide, bypassing local distribution constraints.
- Dedicated schemes: National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM) with target of 5 MMT of Green Hydrogen production annually by 2030; Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme with target of 20% ethanol blending in petrol by 2025-26; National Solar Mission (NSM); National Bioenergy Programme (2021–2026); Waste to Energy Programme; etc.
- Accelerating investment: 100% FDI allowedunder automatic route; RE classified as a sub‑category under RBI's Priority Sector Lending; Sovereign green bonds etc.
- Domestic manufacturing of components: Schemes like Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for High Efficiency Solar PV Modules, Scheme for "Development of Solar Parks and Ultra Mega Solar Power Projects" promote domestic manufacturing.
- E.g., India's solar module manufacturing capacity jumped from 38 GW to 74 GW during FY 2024–25.
- International collaborations:
- International Solar Alliance (ISA): Launched by India and France at COP21 in 2015, brings together 100+ countries to mobilise $1 trillion in solar investments to make clean energy affordable.
- One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG): Launched by India at the ISA Assembly in 2018, aims to create a global interconnected solar grid.
Challenges in realizing true potential of Renewable sector
- Financial & Investment Barriers:
- Low annual investment: India requires around USD 10 trillion by 2070 for its clean-energy transition.
- DISCOM financial distress: DISCOMs suffer from poor billing efficiency, revenue gaps, tariff delays affecting working capital and debt servicing for RE companies.
- Infrastructure Challenges
- Intermittency of Renewables: E.g., Solar peaks during the day but not at evening peak demand forcing states to backstop solar with coal.
- Transmission Bottlenecks: E.g., in states like Tamil Nadu with high wind capacity, power often cannot be fully evacuated because the grid network is congested.
- Limited Storage Capacity: Battery storage cost remains high (~₹5–6 per unit storage cost), making round the clock renewable power costly.
- Land acquisition: Renewable energy projects require large tracts of land, leading to delays, high costs, and conflicts with local communities as well as food security concerns.
- E.g., Solar can need 300 times as much space as nuclear energy (Economic Survey 2023-24).
- Manufacturing Constraints
- Heavy dependence on imports: India imports 80–90% of solar cells and modules from China due to limited domestic polysilicon/wafer manufacturing.
- Global Supply Chain Disruptions: Production and processing of many critical minerals are geographically concentrated, making global supply vulnerable to several risks.
- E.g., China controls 60% of rare earth production, 60% of critical minerals production and 80% of the processing worldwide.
- Other issues: Poor enforcement of RP targets; Inconsistent net metering rules; Environmental concerns related to extraction of minerals
Way Ahead
- Enhance DISCOM reform: Focus on loss reduction, smart metering, tariff rationalisation to improve payment discipline.
- Build Domestic Manufacturing Capacity: India must expand manufacturing of solar modules, wind turbines, batteries and green hydrogen components through PLI schemes to reduce import dependence.
- Promote Advanced Storage Technologies: Large-scale storage solutions like ACC batteries, pumped-storage hydropower and hybrid systems must be expanded.
- Unified renewable energy law: It can ensure clear rules for Power Purchase Agreement enforcement, land acquisition, and grid access to boost investor confidence.
- Increase Financial Mobilization: Explore diversified funding sources like green bonds, multilateral financing, blended finance, and private investments.
- Plan for a just transition in coal‑dependent regions: through Jobs, reskilling, local RE manufacturing.
- Improve Grid Infrastructure and Renewable Integration: Modernize transmission corridors and enable smart-grid systems through AI/ML technologies.






